Breaking Down The Science – How Meloxicam Eases Arthritis Symptoms
It’s important to understand how medications like meloxicam work to alleviate the symptoms of arthritis. Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is commonly prescribed to reduce pain, swelling, and stiffness associated with arthritis. By targeting the underlying inflammation that causes joint pain, meloxicam helps improve mobility and quality of life for individuals suffering from arthritis.
Key Takeaways:
- Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that helps relieve pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
- Meloxicam works by inhibiting enzymes that produce prostaglandins, which are responsible for causing pain and inflammation in the body.
- It is important to follow the prescribed dosage of meloxicam to avoid potential side effects such as stomach ulcers, kidney problems, and cardiovascular issues.
- Common side effects of meloxicam include stomach upset, nausea, dizziness, and headache, while severe side effects may include bleeding in the stomach or intestines.
- Meloxicam is typically prescribed to be taken once daily with food or milk to help reduce the risk of stomach irritation.
- Before starting meloxicam, it is important to discuss any existing medical conditions or medications with a healthcare provider to ensure it is safe and appropriate to use.
- Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is crucial while taking meloxicam to assess its effectiveness and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
Understanding Arthritis
There’s a common misconception that arthritis is a single disease, but the truth is that it refers to a group of more than 100 conditions that cause joint inflammation. The main symptoms include pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can severely impact an individual’s quality of life.
Definition and Types of Arthritis
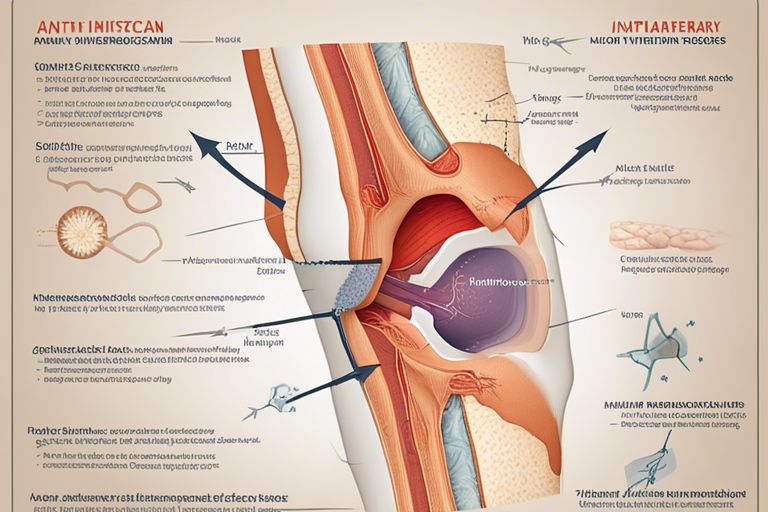
Arthritis encompasses various conditions that affect the joints, resulting in pain and inflammation. Osteoarthritis is the most common type, characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the joints. Other types include gout, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis. The prevalence of arthritis increases with age, affecting millions of people worldwide.
| Osteoarthritis | Breakdown of cartilage |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Autoimmune attack on joints |
| Gout | Build-up of uric acid crystals |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | Inflammation of the spine |
| Psoriatic arthritis | Association with psoriasis |
The exact cause of arthritis varies depending on the type, with factors such as genetics, age, obesity, and joint overuse playing a role. The inflammation in the joints leads to pain and stiffness, impacting mobility and daily activities. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in managing arthritis and preventing disability.
Pathophysiology of Arthritis
Any disruption in the delicate balance of joint structures can trigger arthritis. Inflammation plays a key role in the progression of the disease, causing damage to the cartilage, synovial membrane, and supporting structures around the joint. This chronic inflammatory process can lead to irreversible joint damage if left untreated.
The immune system dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis results in the destruction of joint tissues, leading to deformities and disabilities. Early intervention with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs can help slow down the disease progression and preserve joint function. The severity of arthritis symptoms can vary, with some individuals experiencing mild discomfort while others face debilitating pain and joint deformities.
Meloxicam: An Overview
It is crucial to understand the basics of Meloxicam to appreciate its role in easing arthritis symptoms. Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is commonly used to reduce pain, inflammation, and stiffness caused by various types of arthritis. This medication belongs to the class of drugs known as oxicams and works by inhibiting an enzyme called cyclooxygenase, which is responsible for the production of prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that cause pain and inflammation.
Historical Perspective and Development
An understanding of the historical perspective and development of Meloxicam sheds light on its significance in the field of arthritis treatment. Meloxicam was first developed in the 1980s by Boehringer Ingelheim, a pharmaceutical company based in Germany. It was introduced for medical use in the early 1990s and has since become a widely prescribed medication for managing arthritis symptoms, offering a valuable alternative to other NSAIDs.
Pharmacological Classification
Any discussion about Meloxicam would be incomplete without addressing its pharmacological classification. Meloxicam is classified as a selective COX-2 inhibitor, distinguishing it from traditional NSAIDs that inhibit both cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2). This selective inhibition helps reduce the risk of gastrointestinal complications associated with non-selective NSAIDs, making Meloxicam a preferred choice for many arthritis patients.
To further elaborate, Meloxicam’s selective inhibition of COX-2 enzymes allows it to target inflammation more specifically, leading to effective pain relief with lower risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding compared to non-selective NSAIDs.
Mechanism of Action
All medications have a specific way in which they work in the body to produce their effects. Understanding the mechanism of action of a drug is crucial in comprehending how it helps alleviate symptoms. In the case of Meloxicam, a popular NSAID used for managing arthritis pain and inflammation, its mechanism of action is linked to its ability to inhibit certain enzymes involved in the inflammatory process.
How Meloxicam Works at the Molecular Level
Meloxicam belongs to a class of medications known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs work by inhibiting an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (COX), which plays a pivotal role in the production of prostaglandins – hormone-like substances that contribute to pain, inflammation, and fever. By selectively inhibiting COX-2, Meloxicam helps reduce the levels of prostaglandins at the site of inflammation, leading to a decrease in pain and swelling associated with arthritis.
The Role of Cyclooxygenase Enzymes
COX enzymes exist in two forms: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is involved in maintaining normal physiological functions in the body, such as protecting the stomach lining and promoting kidney function. On the other hand, COX-2 is primarily induced during inflammation and is responsible for producing prostaglandins that contribute to pain and swelling. By selectively inhibiting the COX-2 enzyme, Meloxicam targets the source of inflammation while sparing the COX-1 enzyme, which helps maintain important bodily functions.
Role: This selective inhibition of COX-2 by Meloxicam allows for effective management of arthritis symptoms while minimizing the potential gastrointestinal side effects commonly associated with non-selective NSAIDs, making it a preferred choice for many patients in need of long-term pain relief.
Efficacy of Meloxicam in Managing Arthritis Symptoms
Your journey to understanding how meloxicam eases arthritis symptoms begins with exploring its efficacy in managing the pain and inflammation associated with this debilitating condition. Let’s probe into the two key aspects of its effectiveness in arthritis management: analgesic effects and anti-inflammatory properties.
Analgesic Effects
An necessary component of meloxicam’s efficacy in managing arthritis symptoms lies in its potent analgesic effects. By targeting the pathways that transmit pain signals in the body, meloxicam helps alleviate the discomfort and soreness experienced by individuals with arthritis. This results in a significant improvement in pain relief, allowing patients to regain mobility and enhance their quality of life.
Moreover, meloxicam’s analgesic effects are not just limited to masking the pain; they also contribute to reducing the reliance on other pain medications, making it a valuable treatment option for long-term arthritis management.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Analgesic in nature, meloxicam also possesses robust anti-inflammatory properties that play a pivotal role in managing arthritis symptoms. By targeting the inflammatory response within the joints, meloxicam helps reduce swelling, stiffness, and tenderness, which are hallmark features of arthritis. This dual-action approach of meloxicam in addressing both pain and inflammation sets it apart as a comprehensive treatment for arthritis.
Efficacy studies have demonstrated that meloxicam’s anti-inflammatory properties not only provide symptomatic relief but also help slow down the progression of arthritis, preserving joint function and integrity over time. This makes meloxicam a vital tool in the arsenal against arthritis, offering a ray of hope for those grappling with this chronic condition.
Dosage and Administration
After diagnosing arthritis, it is crucial to understand the proper dosage and administration of meloxicam to effectively manage the symptoms. Meloxicam comes in various forms including tablets, capsules, and oral suspension. The dosage and frequency of administration may vary depending on the type and severity of arthritis.
Recommended Dosages for Different Types of Arthritis
An important aspect of treating arthritis with meloxicam is determining the appropriate dosage for the specific type of arthritis. Below is a breakdown of the recommended dosages for different types of arthritis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: 7.5 mg once daily
- Osteoarthritis: 7.5 mg to 15 mg once daily
- Ankylosing spondylitis: 15 mg once daily
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: 0.125 mg/kg once daily
- Psoriatic arthritis: 15 mg once daily
Perceiving the correct dosage is crucial to ensure optimal relief of arthritis symptoms. Importantly, the information should be followed precisely to avoid any potential risks or complications.
Routes of Administration and Absorption
Dosages of meloxicam can be administered orally or through injection for more severe cases. When taken orally, the drug is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and reaches peak plasma levels within hours. Intravenous administration may be used in cases where immediate pain relief is required.
Routes of administration play a critical role in the effectiveness of meloxicam in managing arthritis symptoms. Understanding how the drug is absorbed and distributed in the body is important for healthcare providers to ensure patients receive the most benefit from the medication.
Safety and Side Effects
Despite its effectiveness in managing arthritis symptoms, it is important to consider the safety and potential side effects of taking meloxicam.
Common Adverse Reactions
Common adverse reactions associated with meloxicam include stomach upset, nausea, heartburn, and headache. Some individuals may also experience dizziness or drowsiness. These side effects are usually mild and tend to improve as the body adjusts to the medication. However, if they persist or become severe, it is important to consult a healthcare provider.
Long-term use of meloxicam can potentially lead to more serious side effects such as ulcers, bleeding in the stomach or intestines, and kidney problems. It is vital to monitor for any signs of these complications, including black stools, stomach pain, or changes in urination, and seek medical attention if any occur.
Considering Long-term Use and Risks
Side effects of meloxicam can increase with long-term use, especially in older adults or those with pre-existing conditions such as heart disease or high blood pressure. It is crucial to regularly review the benefits and risks of continued meloxicam use with a healthcare provider to ensure the best outcomes for arthritis management.
Comparing Meloxicam with Other Arthritis Treatments
Unlike some other arthritis treatments, Meloxicam belongs to a class of medications known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs work by reducing hormones that cause inflammation and pain in the body. When comparing Meloxicam with other treatments, it’s necessary to understand how it stands out in terms of efficacy and safety.
| Traditional NSAIDs Versus Meloxicam | Meloxicam |
| Traditional NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen may cause more stomach irritation and ulcers. | Meloxicam is considered a COX-2 selective NSAID, which may reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. |
| Traditional NSAIDs often require multiple doses per day for symptom relief. | Meloxicam typically requires only once-daily dosing, improving convenience for patients. |
Traditional NSAIDs Versus Meloxicam
Meloxicam, a COX-2 selective NSAID, offers a favorable gastrointestinal safety profile compared to traditional NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen. By targeting specific enzymes involved in inflammation, Meloxicam reduces the risk of stomach irritation and ulcers commonly associated with older NSAIDs. Additionally, the once-daily dosing regimen of Meloxicam enhances compliance and simplifies medication management for individuals with arthritis.
Meloxicam in Relation to Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
With the rise of biologic drugs and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in treating arthritis, Meloxicam plays a different role in symptom management. While DMARDs like methotrexate target the underlying disease process and aim to slow or stop joint damage, Meloxicam focuses on alleviating pain and inflammation. This makes Meloxicam a valuable addition for individuals needing relief from arthritis symptoms while undergoing treatment with DMARDs.
Plus, Meloxicam’s ability to provide targeted relief from arthritis symptoms without interfering with the disease-modifying effects of DMARDs is a significant advantage. By working alongside DMARDs, Meloxicam offers a comprehensive approach to managing arthritis, addressing both pain and underlying disease progression simultaneously.

Conclusion
Hence, it is evident that meloxicam plays a crucial role in easing arthritis symptoms by reducing inflammation and pain. Its mechanism of action, inhibiting COX-2 enzymes, allows for effective management of arthritis symptoms and improved quality of life for those suffering from this condition. Understanding the science behind how meloxicam works can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about its use for arthritis treatment.
In the long run, the science behind meloxicam’s impact on arthritis symptoms provides valuable insight into its efficacy and benefits. By targeting the underlying cause of inflammation, meloxicam offers a promising solution for managing arthritis and its associated symptoms, ultimately improving the overall well-being of individuals living with this chronic condition.
FAQ
Q: What is Meloxicam and how does it help ease arthritis symptoms?
A: Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that works by reducing hormones that cause inflammation and pain in the body. It helps ease arthritis symptoms by decreasing swelling, pain, and stiffness in the joints, making it easier for individuals to move and perform daily activities.
Q: How long does it take for Meloxicam to start working?
A: The time it takes for Meloxicam to start working can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience relief from arthritis symptoms within a few hours of taking the medication, while for others, it may take a few days to a week to feel the full effects. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding the dosage and frequency of taking Meloxicam to achieve the best results.
Q: What are the common side effects of Meloxicam?
A: While Meloxicam is an effective medication for easing arthritis symptoms, it may also cause some side effects. Common side effects of Meloxicam include stomach upset, nausea, heartburn, headache, dizziness, and fluid retention. In some cases, more serious side effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding, high blood pressure, and allergic reactions may occur. It is imperative to consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any concerning side effects while taking Meloxicam.

0 comments